What is Pitted Keratolysis - Explained by Dr. Yeung Ho Hong(楊浩康)
(What is Pitted Keratolysis photo) Created by Samuel Freire da Silva, M.D. in homage to The Master And Professor Delso Bringel Calheiros. Image obtained from Dermatology Atlas.
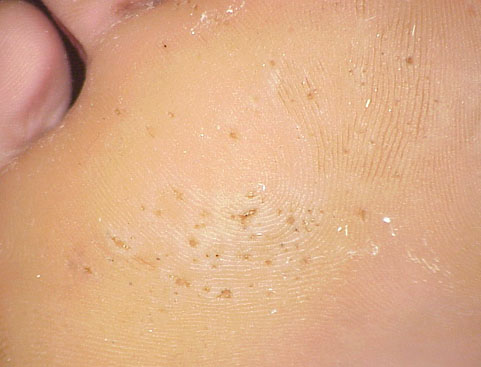
Pitted keratolysis is a superficial bacterial skin infection mainly affecting the soles of the feet characterised by whitish skin with clusters of punched-out pits.
Pitted keratolysis presents as smelly feet (bromhidrosis), and usually affects the sole of the foot. It causes a whitish skin surface with clusters of multiple, fine punched-out pits. Some patients with pitted keratolysis may present with diffuse red areas on the soles. The pits are usually asymptomatic but may cause itchiness or mild pain when walking.
Several bacterial species, including corynebacteria, Dermatophilus congolensis, Kytococcus sedentarius, actinomyces and streptomyces, are responsible for the pitted keratolysis. The bacteria proliferate in moist environment, and will produce protease enzymes which destroy the stratum corneum can cause the formation of the pitting. The sulfur compounds produced by the bacteria cased the bad smell of the feet.
Factors that lead to the development of pitted keratolysis include:hot and humid weather, occlusive footwear, thickened skin of palms and soles, excessive sweating of hands and feet, diabetes mellitus, or immunodeficiency.
Pitted keratolysis can be successfully treated with topical antibiotics, such as erythromycin, clindamycin or fusidic acid, and antiseptics.Treatment of associated hyperhidrosis may be considered to prevent the recurrence of pitted keratolysis.
